BMI Body Visualiser: A revolutionary tool is transforming how we understand and interact with our body mass index. This innovative technology offers a visually engaging approach to interpreting BMI data, moving beyond mere numbers to provide a clearer, more intuitive understanding of individual health. The implications for healthcare, fitness, and education are significant, promising a more proactive and accessible approach to wellness.
By utilizing various visualization techniques, from simple bar graphs to interactive avatars, BMI Body Visualisers aim to make complex health data easily digestible for everyone. This technology not only simplifies the interpretation of BMI but also highlights the limitations of using BMI as a sole indicator of health, encouraging a more holistic approach to wellness. The design and implementation of these visualizers also raise important questions about accessibility, inclusivity, and the ethical considerations of presenting potentially sensitive health information.
Understanding BMI and its Visual Representation: Bmi Body Visualiser
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used indicator of body fat based on height and weight. While not a perfect measure, it provides a valuable screening tool for identifying potential weight-related health risks. Visualizing BMI data enhances understanding and facilitates better health management.
BMI Calculation and Categories
BMI is calculated by dividing an individual’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters: BMI = weight (kg) / height (m)². The resulting number is categorized as follows:
| BMI Range (kg/m²) | Category | Visual Representation Description | Example Avatar Shape |
|---|---|---|---|
| Below 18.5 | Underweight | A thin, light blue bar; a slender avatar. | Tall and thin |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Normal weight | A medium-sized, green bar; a proportionate avatar. | Average height and weight |
| 25.0 – 29.9 | Overweight | A larger, yellow bar; a slightly overweight avatar. | Slightly larger frame |
| 30.0 and above | Obese | A very large, red bar; an overweight avatar. | Considerably larger frame |
Underweight individuals may face health risks such as weakened immunity and bone density issues. Overweight and obese individuals are at increased risk of developing conditions like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers.
Types of BMI Visualizers
Several visual approaches can effectively represent BMI data. Each method offers unique advantages and disadvantages in terms of clarity, user engagement, and accessibility.
Visual Representation Methods
Source: turbosquid.com
Common methods include bar graphs, charts, and avatars. Bar graphs offer a straightforward representation of BMI relative to different categories. Charts, such as pie charts or line graphs, can show BMI changes over time. Avatars provide a more engaging and relatable visualization, representing a person’s body shape based on their BMI.
Bar graphs are simple and easy to understand, but may lack visual appeal. Charts can show trends but can be less intuitive for single data points. Avatars are engaging, but might not be universally understood and could potentially reinforce negative body image perceptions if not carefully designed.
User Interface Mockup
A user-friendly BMI visualiser would begin with clear input fields for height and weight, using metric or imperial units. Upon submission, a progress bar would visually represent the BMI value within the respective category range (underweight, normal, overweight, obese), using colors consistent with the table above. Below the progress bar, a simple avatar would change its shape and size, corresponding to the calculated BMI.
Clear textual labels would accompany the visual representations, stating the calculated BMI and corresponding category.
Data Input and Processing for BMI Visualisation
Accurate data input and robust processing are crucial for a reliable BMI visualiser. The system must handle various data formats and implement error checks to prevent inaccurate results.
Data Acquisition and Algorithm
User data (height and weight) can be obtained through direct input fields, integration with wearable devices, or through APIs from health apps. The BMI calculation algorithm, as described above, is straightforward. The visual representation is generated by mapping the calculated BMI to predefined visual parameters (bar length, avatar size and shape, color).
Error Handling and Data Validation, Bmi body visualiser
The system should validate user inputs, ensuring they are numerical and within reasonable ranges. Error messages should guide users to correct invalid inputs. For instance, if a user enters a negative height or weight, an appropriate error message will appear, prompting the user to input valid values. The system could also include a range check, ensuring that the input values are within realistic human ranges.
Notice henrico jail east inmate search for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in BMI Visualisation
Accessibility and inclusivity are paramount to ensure that all users can benefit from a BMI visualiser. This includes catering to users with visual impairments and avoiding potential biases in the visual representation.
Accessibility Features
For users with visual impairments, alternative text descriptions should accompany all visual elements. Screen readers should be able to interpret the visual data and convey it verbally. Color contrast should be sufficient to ensure readability for users with low vision. Keyboard navigation should be implemented for those who cannot use a mouse.
Mitigating Bias
BMI can be a culturally biased metric, as body composition varies across populations. The visualiser should avoid using imagery that promotes unrealistic body ideals. Providing context and additional information about BMI limitations can help mitigate potential negative impacts on body image.
- Use clear and simple language in all instructions and feedback.
- Provide alternative visual representations to cater to diverse preferences.
- Ensure color contrast meets accessibility guidelines.
- Offer options for customizing the visual representation (e.g., avatar type).
- Include information about the limitations of BMI as a health indicator.
Potential Applications and Benefits of a BMI Visualiser
A BMI visualiser can be a powerful tool in various settings, offering significant benefits over numerical data alone.
Applications and Benefits
| Application Area | Benefit 1 | Benefit 2 | Benefit 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Improved patient engagement and understanding | Facilitates better communication between doctors and patients | Supports weight management programs |
| Fitness Apps | Motivates users to track their progress | Provides visual feedback on the effectiveness of exercise and diet plans | Enhances user engagement and adherence to fitness goals |
| Educational Materials | Makes complex health information more accessible and engaging | Improves understanding of BMI and its implications | Promotes healthier lifestyle choices |
Limitations and Considerations of BMI Visualisers
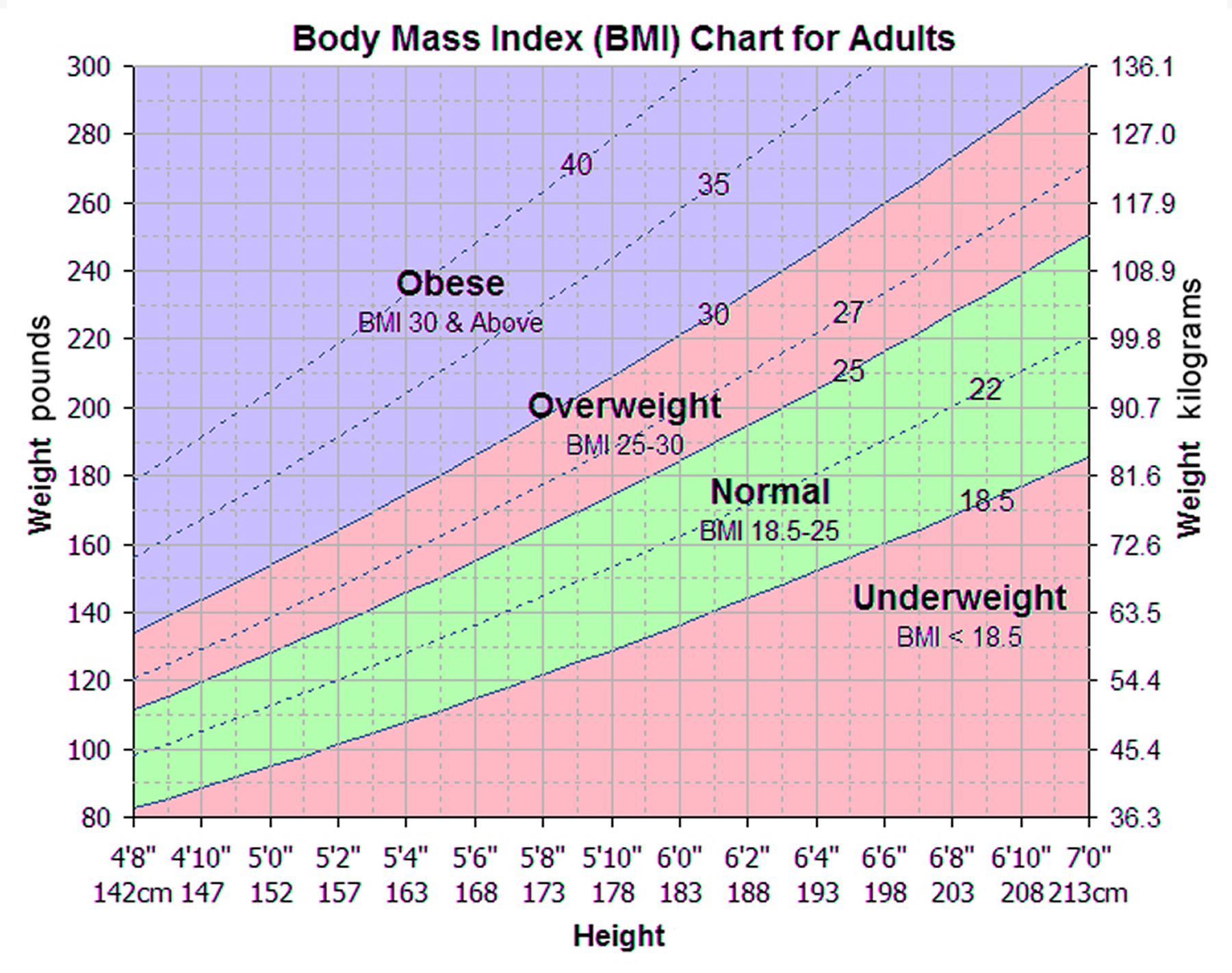
Source: healthjade.net
While BMI visualisers can be beneficial, it’s crucial to acknowledge their limitations and potential ethical concerns.
Limitations and Ethical Considerations
BMI is not a perfect measure of health and should not be used in isolation. It does not account for muscle mass, bone density, or body fat distribution. Over-reliance on BMI can lead to inaccurate assessments and potentially harmful body image issues, particularly for individuals with higher muscle mass or specific body types.
- Body fat percentage
- Waist circumference
- Hip-to-waist ratio
Ending Remarks
BMI Body Visualisers represent a significant advancement in health technology, offering a powerful tool for promoting health awareness and encouraging healthier lifestyles. While limitations exist, and ethical considerations must be addressed, the potential benefits of these visualizers—particularly in improving understanding and accessibility of health data—are undeniable. Further development and responsible implementation of this technology will be crucial in ensuring its widespread positive impact.